Table of Contents
A for loop is used to iterate (or loop) through a sequence — such as a list, tuple, string, or range of numbers. Similar to the for loop in other programming languages, the for loop runs a block of code multiple times — once for each item in a sequence.
There are different methods to use a for loop.
1. Looping with range()
The range() function generates a sequence of numbers that is perfect for looping a fixed number of times.
Write a Python program to print “Hello World” five times using a for loop.
for i in range(5):
print("Hello World")
# output
# Hello World
# Hello World
# Hello World
# Hello World
# Hello World
| Iteration | value of i | Action | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | i = 0 | Execute(print statement) | Hello World |
| 2 | i = 1 | Execute(print statement) | Hello World |
| 3 | i = 2 | Execute(print statement) | Hello World |
| 4 | i = 3 | Execute(print statement) | Hello World |
| 5 | i = 4 | Execute(print statement) | Hello World |
| Stop | i = 5 | Loop condition is met | - |
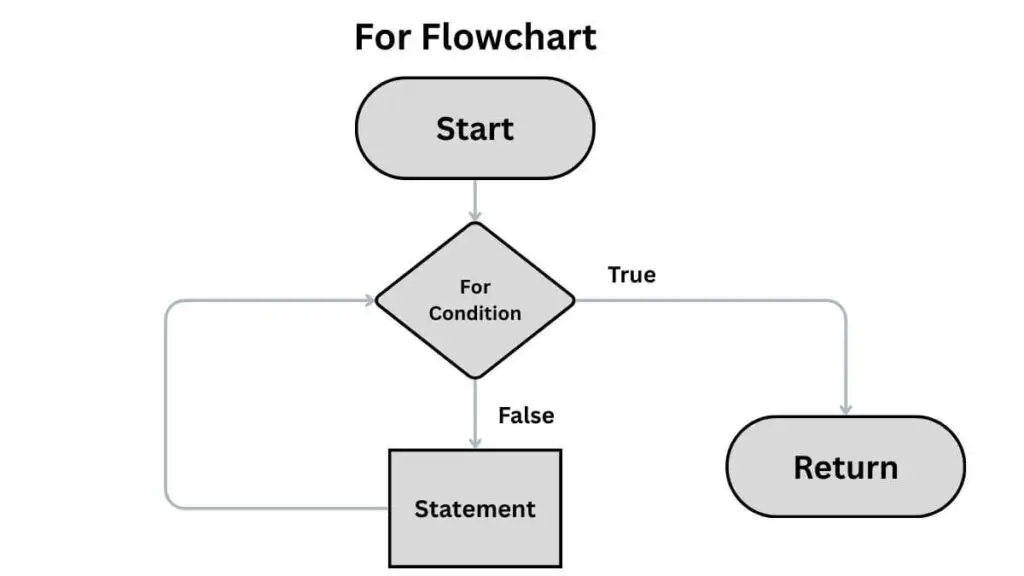
2. Loops using range and Custom Range in for Loops
The range() function is a built-in function used to generate a sequence of numbers for a loop to iterate over. The range function starts from 0 by default and increments by 1 for each iteration. If the range is given as range(5) then the output is 0 to 4 (one number less than what is specified in the function.)
Its primary role is to control how many times a loop executes and to provide a sequence of indices or values for the loop variable to take on during those iterations.
We can also have our custom range in for loops we have to specify the numbers from start to end in the range. If we specify the range as (1, 6) it will print numbers from 1 to 5 and will exclude 6.
a)Write a Python program to print numbers till five.
b)Write a Python program to print numbers from 10 to 15 using a for loop.
# a)
for i in range(6):
print(i)
# output
# 0
# 1
# 2
# 3
# 4
# 5
# b)
for i in range(10, 16):
print(i)
# output
# 10
# 11
# 12
# 13
# 14
# 15
| Iteration | Value of i | Action | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | i = 0 | Execute Print(0) | 0 |
| 2 | i = 1 | Execute Print(1) | 1 |
| 3 | i = 2 | Execute Print(2) | 2 |
| 4 | i = 3 | Execute Print(3) | 3 |
| 5 | i = 4 | Execute Print(4) | 4 |
| 6 | i = 5 | Execute Print(5) | 5 |
| Stop | i = 6 | Loop Terminates | - |
| Iteration | Value of i | Action | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | i = 10 | Execute Print(10) | 10 |
| 2 | i = 11 | Execute Print(11) | 11 |
| 3 | i = 12 | Execute Print(12) | 12 |
| 4 | i = 13 | Execute Print(13) | 13 |
| 5 | i = 14 | Execute Print(14) | 14 |
| 6 | i = 15 | Execute Print(15) | 15 |
| Stop | i = 16 | Loop condition is met (Range is exhausted brfore 16) | - |
3. Looping through Strings.
Looping through strings is a programming technique used to access and process each character within a string one by one, from the beginning to the end. The loop treats the string as an ordered collection of elements (characters).
It is the standard method for performing character-level analysis or transformations, such as:
- Counting specific letters (vowels, consonants).
- Searching for substrings or delimiters.
- Building a new, modified string (e.g, reversing the original string).
Write a Python program to print individual characters from the word “Python” one below the other.
my_string = "Python"
for char in my_string:
print(char)
# output
# P
# y
# t
# h
# o
# n
| Iteration | Value of char | Action | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 'P' | Execute print(P) | P |
| 2 | 'y' | Execute print(y) | y |
| 3 | 't' | Execute print(t) | t |
| 4 | 'h' | Execute print(h) | h |
| 5 | 'o' | Execute print(o) | o |
| 6 | 'n' | Execute print(n) | n |
| Stop | (end of string) | The loop condition is met | - |
The loop iterates through each character of the string assigning it to char, and prints the individual characters at the same time.
4. Break Statements in a For Loop
The loop is immediately stopped when it encounters a break statement.
for num in range(10):
if num == 5:
break
print(num)
# output
# 0
# 1
# 2
# 3
# 4
In the above code the loop is terminated once num is equal to five.
5. Continue Statement
Continue statement skips the specified iteration and jumps to the next.
for num in range(10):
if num == 5:
continue
print(num)
# output
# 0
# 1
# 2
# 3
# 4
# 6
# 7
# 8
# 9
In the above code the loop skips the iteration when num is equal to five and continues with the next iterations.
6. Python Nested For Loops
We can run loops inside loops especially for multidimensional data. There is an Outer Loop and an Inner Loop. The Inner Loop must complete all of its iterations for every single iteration of the Outer Loop.
Write a Python program to print the pattern shown below.
*
* *
* * *
* * * *
* * * * *
for i in range(1, 6):
for j in range(i):
print("*", end=" ")
print()
# output
# *
# * *
# * * *
# * * * *
# * * * * *
| Outer Loop (i) | Inner Loop Range | Inner Loop Runs (Times) | Output Action | Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | range(1) | 1 | Prints *, then newline | * |
| 2 | range(2) | 2 | Prints * *, then newline | * * |
| 3 | range(3) | 3 | Prints * * *, then newline | * * * |
| 4 | range(4) | 4 | Prints * * * *, then newline | * * * * |
| 5 | range(5) | 5 | Prints * * * * * | * * * * * |
| 6 | loop terminates |
Practice Questions
Try the questions below by yourself and check the results below.
1. Write a Python program to add numbers in a range using a for loop
total = 0
for num in range(1, 11): # adds 1 to 10
total += num
print("Sum =", total)
# Sum = 55
The above program adds numbers from 1 to 10 by using for loop.
initialization: total = 0
Loop Setup: for num in range(1, 11): creates a loop that iterates through the numbers generated by range(1, 11), which are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
Accumulation: total += num executes on each iteration, adding the current value of num to total. All the added values are stored here
2). Write a Python program to print the Fibonacci series using Python
n = 10
a, b = 0, 1
print("Fibonacci Series:")
for _ in range(n):
print(a, end=" ")
a, b = b, a + b
# Fibonacci Series:
# 0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34
| Loop Iteration | a Value (Start) | b Value (Start) | print(a, end=" ") Output | a, b = b, a + b (New a, New b) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initialization | 0 | 1 | Fibonacci Series: | - |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | a=1, b=1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | a=1, b=2 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | a=2, b=3 |
| 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | a=3, b=5 |
| 4 | 3 | 5 | 3 | a=5, b=8 |
| 5 | 5 | 8 | 5 | a=8, b=13 |
| 6 | 8 | 13 | 8 | a=13, b=21 |
| 7 | 13 | 21 | 13 | a=21, b=34 |
| 8 | 21 | 34 | 21 | a=34, b=55 |
| 9 | 34 | 55 | 34 | a=55, b=89 |
| Loop End | 55 | 89 | - | Loop terminates. |
3) Write a Python Program for String Reverse in Python Using a for Loop
text = "python"
reverse = ""
for ch in text:
reverse = ch + reverse # prepend each character
print("Reversed:", reverse)
# Reversed: nohtyp
| Iteration | ch (Current Char) | reverse (Before) | ch + reverse (New reverse) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 'p' | " " | 'p' + "" = 'p' |
| 2 | 'y' | 'p' | 'y' + 'p' = 'yp' |
| 3 | 't' | 'yp' | 't' + 'yp' = 'typ' |
| 4 | 'h' | 'typ' | 'h' + 'typ' = 'htyp' |
| 5 | 'o' | 'htyp' | 'o' + 'htyp' = 'ohtyp' |
| 6 | 'n' | 'ohtyp' | 'n' + 'ohtyp' = 'nohtyp' |
4. Write a Python program to find the factorial of a number.
num = 5
fact = 1
for i in range(1, num + 1):
fact *= i
print("Factorial =", fact)
# Factorial = 120
| Iteration | i value | fact (before) | fact *= i (Calculation) | fact (After) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 * 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 * 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 * 3 | 6 |
| 4 | 4 | 6 | 6 * 4 | 24 |
| 5 | 5 | 24 | 24 * 5 | 120 |
5. Write a Python program to find whether the entered string is a palindrome using a for loop.
text = "madam"
reverse = ""
for ch in text:
reverse = ch + reverse
if text == reverse:
print(text, "is a palindrome")
else:
print(text, "is not a palindrome")
# madam is a palindrome
For the analysis of the code refer to the third question above( reverse the string). If the reverse of the string is equal to the original string then it is considered a palindrome.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. How to iterate a for loop through a list?
fruits = [“apple”, “banana”, “cherry”]
for fruit in fruits:
print(fruit)
# apple
# banana
# cherry
2. What is the difference between for and while loops in Python?
A for loop runs a fixed number of times or through a known sequence, while a while loop continues to run until a condition becomes false. Use for when you know the iteration count, and when you don’t.
3. Can I use a for loop with a dictionary in Python?
Yes! You can loop through a dictionary’s keys, values, or key-value pairs using .keys(), .values(), or .items() respectively.
4. How can I make my for loop run faster in Python?
To optimize your loop, use list comprehensions, built-in functions (like sum() or map()), and avoid performing heavy operations inside the loop.
5. What is a nested for loop in Python?
A nested for loop means placing an inner for loop inside an outer for loop. It’s commonly used to work with multi-dimensional data structures like matrices or grids.
